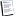 Excel range coding in DLL
Excel range coding in DLL
Typo -
If you mean unregister from Windows, remove from Com-Addins then
Start/Run Regsvr32 /s, browse to the dll, add "/u"
or similar with Shell but embrace the name with apostrophes
- or similar with Shell but embrace the full-name with QUOTES
Which means double quotes or Chr(34) when making the string
Peter T
"Peter T" <peter_t@discussions wrote in message
...
Comments in line
I have couple of questions about VB6 COM addin
. As quite newbee on this subject I create DLL ,reference it on
Excel.But as most are being test DLL I'like to delete them rather
than dereferencing. I do not know how to.
Not sure what you mean by "dereferencing"
If ticked under tools References in a vba project, un-tick it.
If you mean unregister from Windows, remove from Com-Addins then
Start/Run Regsvr32 /s, browse to the dll, add "/u"
or similar with Shell but embrace the name with apostrophes
Don't delete the dll before doing the above as appropriate.
. Will I use the only file which has a extention "dll" if I want to
use it on other PC as
VB6 produce other files as well along with "dll" extentioned one?
Only distribute the dll, the others are your project files
. I put simple functions that I call from my excel code they work
great. How can I
make use of below excel VBA routine in my DLL.
If Not Intersect(Target, Me.Range("C:C")) Is Nothing Then
Call operatornamematch(Target)
Target.Offset(, -2).Value = Worksheets("tr2007").Range("B2")
Target.Offset(, -1).Value = Worksheets("tr2007").Range("B11")
Target.Offset(, 3).Value = Target.Offset(, -2).Value &
Target.Offset(, -1).Value & Target.Value
Target.Offset(, 4).Value = Target.Offset(, -2).Value &
Target.Offset(, -1).Value
End if
You'll need to prefix any specific Excel-VBA functions with a ref to xl
If Not xlApp.Intersect(etc
When you declare any Excel objects prefix with the application name
Dim Target as Excel.Range
and similar in procedure arguments
I use a wrapper to invoke DLL functions once Peter Beach suggested
such as
Option Explicit
Private m_objMyThing As TestCOMDLL.TestClass
Public Function TestWrapper1(ByVal a_nNumber as Double) As Double
If m_objMyThing Is Nothing Then Set m_objMyThing =
CreateObject("TestCOMDLL.TestClass")
TestWrapper1 = m_objMyThing.DoubleIt(a_nNumber)
End Function
This looks fine providing the dll is registered on the user's system. That
occurs automatically if once loaded as a Com-addin, if not you'll need to
use Regserv32. Also, TestClass should be a public class.
Regards,
Peter T
|